Trade Finance Solutions for Africa
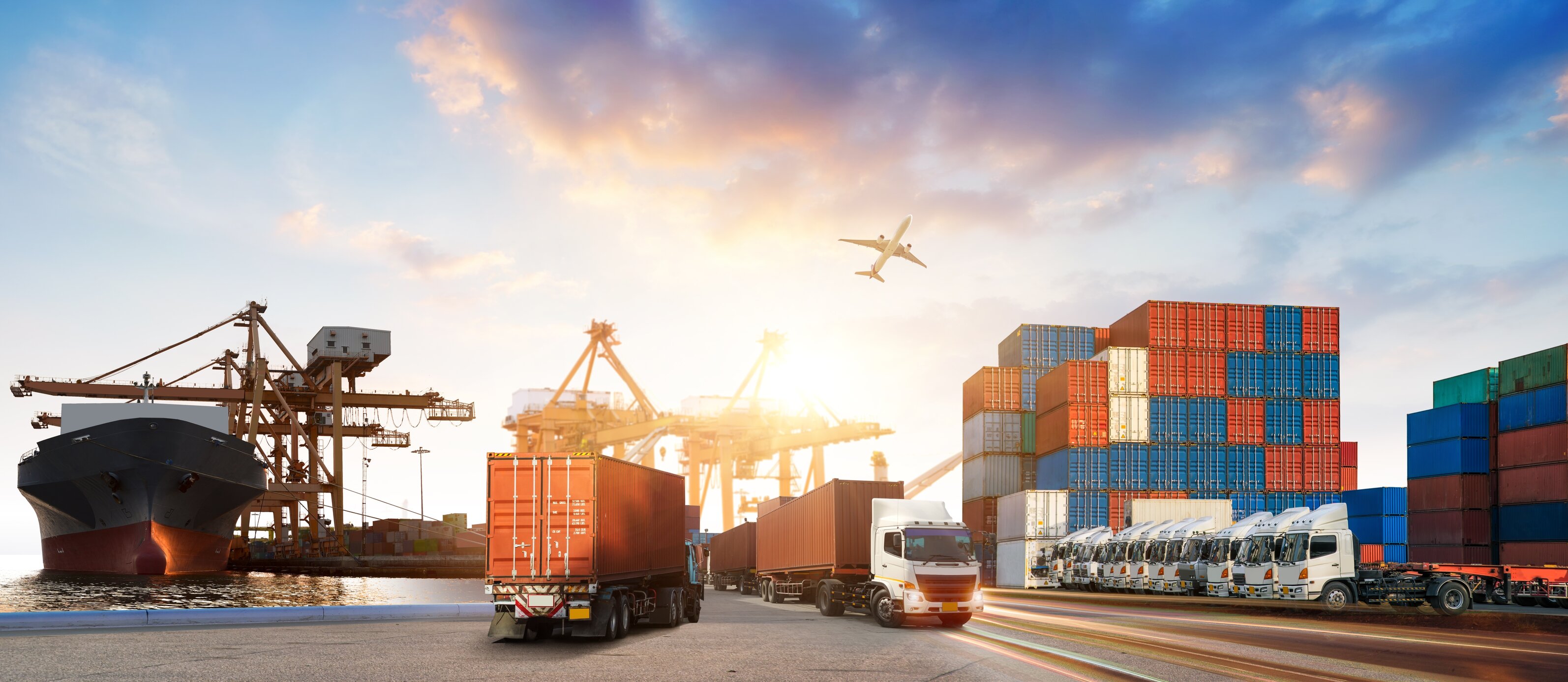

For businesses entering the global trade arena, trade finance solutions provide the vital financial lifeline needed to help contribute towards a growing economy. According to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), “Trade finance serves as the lifeblood of the day- to-day international trade”. They can be likened to a bridge of sorts that connects exporters and importers, providing stability in the domain of international trade and helping to ease the buying and selling of goods. On one end, these financial instruments ensure that exporters receive payment for their goods and services, and on the other, importers gain the ability to secure timely deliveries of their interests. This is all facilitated through bespoke finance solutions such as letters of credit, bank guarantees and supply chain financing.
The Importance of trade finance in Africa
As a continent with significant economic potential, trade finance solutions are particularly important in Africa. They provide the ability for the aforementioned solutions to be accessed, contributing to inter-regional collaboration by promoting the growth and expansion of its competitive businesses. One thing that external factors have made apparent is the precarious nature of global trade. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) estimated that COVID-19 resulted in a worldwide reduction in GDP and, similarly, a contraction in global trade by 3.4% and 10.9, respectively. We must learn from this tumultuous era and recognise how easily global trade can be impeded and derailed. Therefore, for African countries with such vast potential for economic growth, trade finance solutions can act as a meter for course correction, ensuring that its businesses and economies stay on track and reach the desired destination of increased inter-regional trade.
Purpose of the blog
In this post, an overview of African trade finance solutions will be provided. The challenges that hinder trade finances on the continent will be discussed, and in doing so, we will explore the potential solutions required to overcome such obstacles.
The challenges of prohibiting Trade Finance in Africa
Political instability and regulatory issues
To foster any growth, and reap the benefits of a well-developed society, a stable foundation and a strong economy is required. However, political instability directly impedes the potential growth of African countries by limiting access to trade finance. This uncertainty fostered in businesses is unpredictable, and these political climates create shifting foundations that often lead to regulatory changes. This ever-changing landscape, therefore, acts to deter foreign investors, detrimentally affecting trade finance transactions.
Lack of financial infrastructure
Even with the stable foundation required to foster trade financing, many African countries lack the essential financial infrastructure necessary to support trade finance. The combination of limited access to formal financial services, weak credit systems and inadequate banking networks all work in tandem to limit trade finance access. This infrastructure gap hinders businesses and, ultimately, the associated African countries from participating in international trade.
High risk perception
Now consider an environment skewed towards political instability and tied to a network of inadequate financial infrastructure. Factors such as these significantly contribute to the high-risk perception of African countries, leading to limited access to trade finance. The 2015 Ernest and Young survey on attractiveness attributed corruption, weak security and poor basic infrastructure as the main barriers to African investment (26%, 21.9% and 13.6%, respectively). Other factors, such as economic uncertainty due to natural disasters and weak legal frames, also contribute to African markets being perceived as risker by influential financial institutions. Which, therefore, makes it difficult for African businesses to secure trade finance at competitive and fair rates.
Implementing Know your Client and Anti-Money Laundering procedures
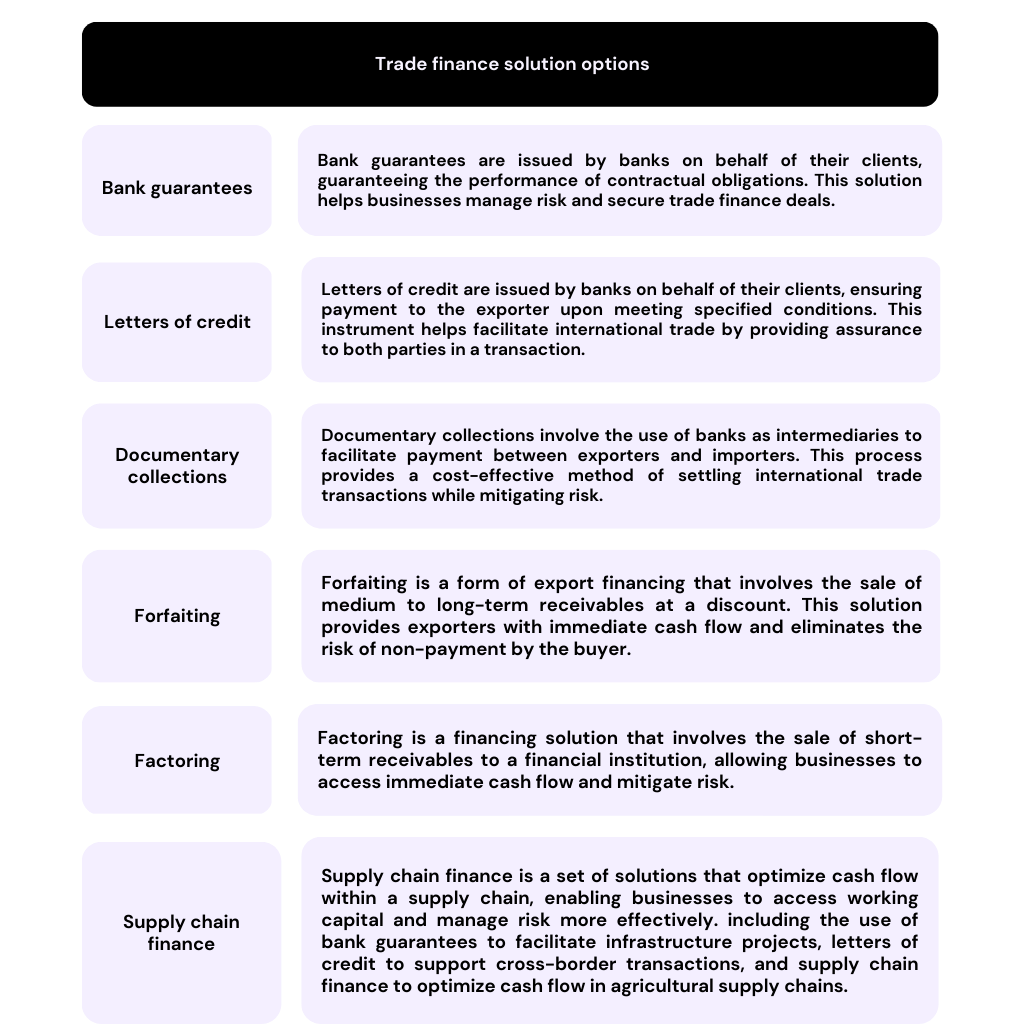
> African Trade Finance Overview of African trade finance market The current African trade finance market can be described as diverse and fragmented. Where across the continent, different countries have varying access to trade finance solutions. Whilst some countries have well-developed financial markets (South Africa, Mauritius and Nigeria ), others struggle to provide their businesses with essential trade finance instruments. The major players in the African trade market mirror this fragmentation. Where to gain trade finance, access is required to traditional institutions such as local and international banks, development finance institutions and export credit agencies. These organisations provide various trade finance solutions, such as loans, guarantees, and risk mitigation products. However, the scale of these divided networks contributes to splintering access to vital finance avenues that could help fund many African businesses. Current trends in African trade finance The solution to this fragmented market, is held in promoting the growing trend of inter-regional collaboration and actualised through initiatives such as the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA). The AfCFTA aims to create a single market for goods and services, and these aims are expected to boost intra-African trade by driving the demand for trade finance solutions. In adopting a more uniform and coherent trade landscape, digitised solutions such as fintech also have a higher likelihood of success across the African continent. Therefore, the main trends that must be promoted in the emerging African region are ones that foster seamless trade solutions that integrate seamlessly with businesses and encourage collaboration within the continent. Opportunities in African trade finance Despite its apparent problems, the African trade finance market presents many new and exciting opportunities. With the advent of the AfCFTA, a stable economic foundation is forming which promotes the growth of intra-African trade. This increased inter-regional trade of African businesses will be carried out on platforms such as ATEX, which operate as digital networks for trading while offering helpful trade financing solutions. Afreximbank also plays a crucial role in financing international trade by mobilising and allocating vital resources for its member countries. The unmet trade finance gap within Africa was estimated to be 120 Billion USD. To meet this demand, organisations like Afreximbank offer many financial solutions through finance solution programmes such as structured trade finance, Note purchases , factoring and asset-backed lending. The procedure for accessing these trade finance facilities is robust but relatively simple and is tailored for each solution: • Research the available options suitable for your enterprise • Prepare the necessary documentation and identify a partner bank that operates withing your region. • Submit your application and the corresponding documents to the partner bank • After awaiting approval sign the necessary agreements • Access your required trade finance solution to support your trade activities. More in-depth information for the guidelines and procedures to accessing the Trade Finance programme can be found on the Afreximbank website. Export-Import Financing in Africa Overview of export-import financing Export-import financing refers to the set of financial solutions that support international trade transactions. Export financing assists exporters in managing cash flow and mitigating risk, while import financing helps importers secure the necessary funds to purchase goods and services from overseas suppliers. We should look at the current case of Kenya and Tanzania as they offer an insight into the potential future of export-import financing in Africa. The AfDB 2022 June report on trade finance demand and supply in Africa recognises a robust positive correlation between increased trade finance and increased export sales per year. Furthermore, the unmet trade finance demand of Kenya and Tanzania are $3 billion and 1.3 billion. Resulting in a lost value in trade of $80,107 and $24,966 a year per firm, respectively, due to a lack of easy access to finance solutions. With this in mind, it is apparent that many SMEs within the African continent have their growth stifled by constraining bank guidelines that often lead to trade finance application rejections. In recognising this, for a truly fair financial environment and one that is competitive for all, innovative policies and schemes should be used that modernise the export and import solutions below. Trade Finance Solutions for Africa Advantages and disadvantages of trade finance solutions Trade finance solutions offer various advantages, such as improving cash flow, managing risk, and facilitating international trade. In the case of the Banco de Fomento Angola (BFA), Afreximbank provided a $50-million line of credit to the Angolan bank to support and fill the gap created by the withdrawal of international banks. This allowed the bank to support SMEs across Angola with financial support and contribute to increasing intra-African trade within the continent. However, disadvantages such as high costs, complex documentation requirements and the potential for fraud often arise when accessing these solutions and invertedly damage the potential growth of African businesses. Therefore, in order to maximise future African trade solutions, traditional institutions and methods such as the Bank guarantees and letters of credit highlighted below must be well advertised and updated to be easily accessible. In doing so, reflecting the new direction of an efficient and integrated AfCFTA region. Strengthening risk mitigation techniques To fully realise the potential of the African market, risk mitigation techniques must be improved with the intended goal of supporting the expansion of trade finance. Without adequate risk management, recipients of trade finance solutions will suffer the most, mainly from fluctuating exchange rates. Therefore, it is crucial for institutions to improve risk management techniques as it facilitates secure transactions, boosts investor confidence and provides more accessible trade finance avenues to many African businesses. Effective risk management contributes to a strong financial system in any economy. It doesn't necessarily guarantee that they won't fail, but it helps identify and neutralise potential threats, thus promoting their overall health and resilience. Some essential techniques include KYC/ AML procedures, embracing innovative fintech solutions and utilising trade finance instruments such as letters of credit and credit insurance. By refining and advancing risk mitigation techniques, Africa can foster a stable and transparent trade finance environment and empower businesses to participate in international trade confidently. Final thoughts and recommendations The goal of any competitive business is to participate in global trade and expand into new markets. With this in mind, the importance of in African Trade finance cannot be stressed enough, as it is the fuel that directly propagates the economic growth of the African continent. This growing demand for trade finance in Africa reflects the continent's appetite for economic progression and the need for financial solutions that cater to its unique challenges. Whilst these obstacles, such as political instability and inadequate financial infrastructure remain, opportunities exist to improve access to trade finance through digital innovation, regional integration, and partnerships between local and international financial institutions. The future of trade finance in Africa is promising, with the potential for significant growth and development. Therefore to fully capitalise on the opportunities in the African trade finance market, businesses and financial institutions should: 1. Embrace digital innovations and technologies to streamline trade finance processes and improve access to financing. 2. Encourage regional integration and collaboration to create a more unified and conducive environment for trade finance. 3. Foster partnerships between local and international financial institutions to leverage expertise and resources for the benefit of African businesses. 4. Strengthen regulatory frameworks and promote political stability to reduce risk perception and attract investment in the region. By addressing the challenges and harnessing the opportunities in African trade finance, businesses can contribute to the continent's economic growth and development, fostering a more prosperous future for Africa.